What are Core Web Vitals? How to Improve Your User Experience?
Estimated reading time: 6 minutes
Did you know that user experience is one of the ranking factors of Google? That's right.
But how does Google determine whether users have a positive or negative experience? For this, Google has introduced core web vitals, a quality ranker for your website's speed.
In this post, read about what the core web vitals are, their significance, and how you can improve your website's user experience.
Let's get started!
Reach out to us for a free SEO audit with our SEO consultants.
What are Core Web Vitals?
Here are the Core Web Vitals you need to know about user experience:
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): This metric gauges how long it takes for a web page's primary content to load for consumers. Google recommends an LCP of less than 2.5 seconds.
Initial Input Delay (FID): FID gauges how quickly a user may interact with a web page after their initial visit. This covers button presses, link clicks, and unique JavaScript actions. An FID of < 100 milliseconds is what Google advises.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): This counts the number of layout changes that force the web page's primary content to move. The user's ability to fully interact with the page and read the content is affected by these changes. A CLS score of 0.1 or lower is what Google recommends.
Why Core Web Vitals Are Important?
According to Google, a web page that takes one to five seconds to load has a 90% rise in bounce rates.
Further, Google's search algorithm also includes Core Web Vitals and the page experience as one of the ranking factors.
That is why, improving your LCP, FID, and CLS will help your site rank high on mobile search results pages. Moreover, organic traffic can increase significantly with merely a single place on the top page of search results.
Likewise, by encouraging positive reviews, referrals, and repeat businesses, improving user experience can lead to a significant boost in business.
Core Web Vitals Measurement Tools
From Google PageSpeed Insights and Google Search Console, you can generate a report for your website to get a glimpse into your website's Core Web Vitals.
PageSpeed Insights
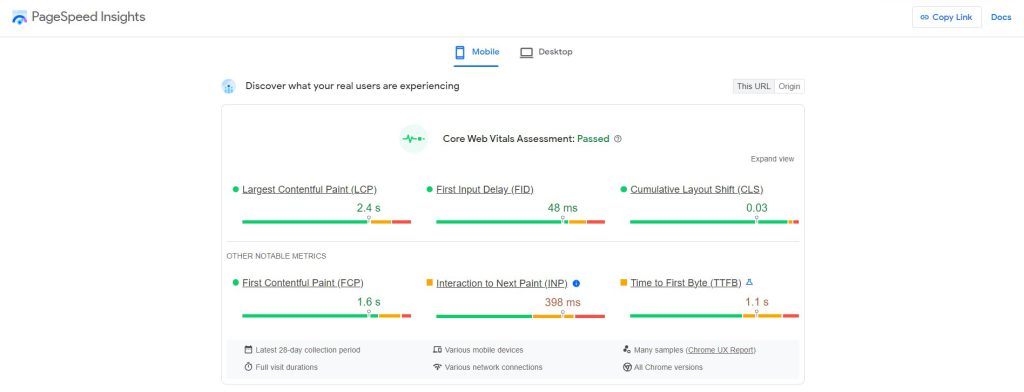

PageSpeed Insights evaluates your website's performance and offers tips for accelerating it. It examines each of the three Core Web Vitals in both desktop and mobile browsers. The field data is the data from the Chrome User Experience Report that relates to actual users.
Google Search Console
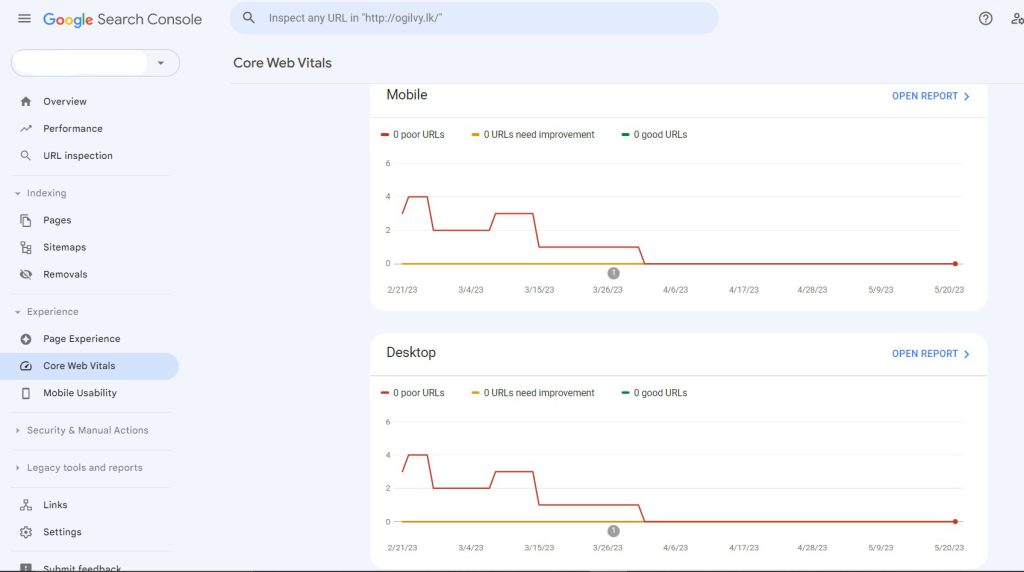

You may find Core Web Vitals for your web pages in Google Search Console. The information from the Chrome User Experience Report is used by Google Search Console to show you problems on your entire website.
GTMetrix
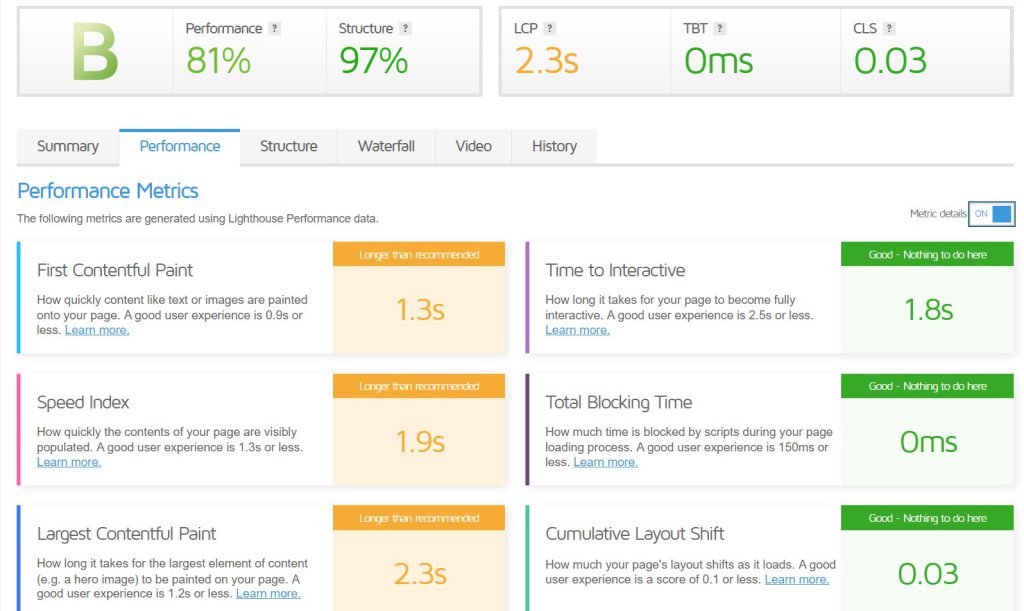

GTmetrix is also another tool from which you can generate a detailed core web vitals report and a performance report similar to page speed insights.
Read More: How to Increase Website Page Speed? (Tips+Tools)
How to Optimize the Largest Contentful Paint
For website optimization and raising the Largest Contentful Paint metric for your web pages, Google provides a number of recommendations.
1. Make changes to your web server
Your web server should come first. It may be time to switch from a shared to a dedicated server if you are encountering significant delays.
Think about any processes that are currently active on your website that could be disabled or improved for performance.
By deleting unwanted or outdated plugins from a WordPress website, for instance, you can lower the number of operations your database handles.
2. Utilize a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
Utilizing a Content Delivery Network (CDN) is the second piece of advice provided by Google. In some cases, hosting plans for businesses come with CDN services.
Tip: You can use services like Google Cloud or Cloudflare to distribute your content across multiple servers across the world and speed up load times. No matter how far away from your web server users are located, CDN services make sure your website loads swiftly.
3. Cache
Cache your material next, and HTML pages will be served from the cache first. When your static HTML content is cached, a user won't have to wait for it to load every time they access your website.
If you use WordPress, you can automatically cache the content for quicker loading by using caching plugins like W3 Total Cache or WP Fastest Cache.
4. Minify CSS, Javascript
In addition to "minifying" (removing extraneous characters from style sheets and scripts), eliminating redundant code, and moving code not required for the initial loading of a web page to a preloaded resource are further approaches to optimize both JavaScript and CSS. Consider adding the most important code online.
Google suggests using CSSnano, csso, and UglifyJS to minify CSS and JavaScript, respectively. The HTML Minifier also allows you to minify HTML.
The Coverage function in Google Chrome DevTools examines how much CSS and JavaScript are being used on your website. If it is not already being utilized by another component of your tech stack, it can identify code that can be offloaded to a preloaded resource.
How to Reduce First Input Delay
Optimizing your JavaScript and using third-party scripts will help your website's First Input Delay time. The latter often make use of online analytics programs and any code that invokes script from another website.
As already noted, you can reduce the amount of JavaScript utilized by minifying (eliminating superfluous characters from scripts), removing unused code, and moving code not required for the initial loading of the web page to a preloaded resource.
To locate code that can be offloaded to a resource that has already been loaded, use Google Chrome DevTools' Coverage function.
The Best Ways to Enhance the Cumulative Layout Shift
If you want your web pages to receive a higher CLS score, you must instruct the browser how much space to dedicate for elements as they load. You can achieve this by giving images and videos particular size properties.
As an alternative, aspect-friendly ratio boxes are available in CSS. Both will succeed in preventing an unexpected change in content during page load.
Use on-page indications for elements that move when loaded when a user interacts with the website. The user may not click on shifting items if they are informed that they are loading on the page.
Read Next: Web Accessibility: Why Is It Important & Best Practices




